All::Ophthalmology::Diseases::Acute angle-closure glaucoma
Intro
What is Acute angle-closure glaucoma?
Acute angle-closure glaucoma (AACG) there is a rise in IOP secondary to an impairment of aqueous outflow
Risk factors for Acute angle-closure glaucoma?
- hypermetropia (long-sightedness)
- pupillary dilatation
- lens growth associated with age
What are the symptoms of Acute angle-closure glaucoma?
- severe pain: may be ocular or headache
- decreased visual acuity
- symptoms worse with mydriasis (e.g. watching TV in a dark room)
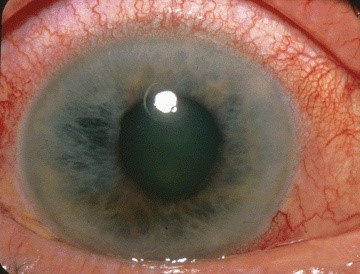
- hard, red-eye
- haloes around lights
- semi-dilated non-reacting pupil
- corneal oedema results in dull or hazy cornea
- systemic upset may be seen, such as nausea and vomiting and even abdominal pain
What are the investigations of Acute angle-closure glaucoma?
- tonometry to assess for elevated IOP
- gonioscopy (literally looking, oscopy, at the angle, gonio): a special lens for the slit lamp that allows visualisation of the angle
What's the management of Acute angle-closure glaucoma?
- An emergency and should prompt urgent referral to an ophthalmologist
- Emergency medical treatment is required to lower the IOP with more definitive surgical treatment given once the acute attack has settled.
Definitive management - laser peripheral iridotomy (creates a tiny hole in the peripheral iris)
How does optic timolol work for Acute angle-closure glaucoma?
decreases aqueous humour production
What medication groups are used in acute treatment of Acute angle-closure glaucoma?
- a direct parasympathomimetic (e.g. pilocarpine, causes contraction of the ciliary muscle → opening the trabecular meshwork → increased outflow of the aqueous humour)
- a beta-blocker (e.g. timolol, decreases aqueous humour production)
- an alpha-2 agonist (e.g. apraclonidine, dual mechanism, decreasing aqueous humour production and increasing uveoscleral outflow)